The semiconductor industry has quietly emerged as one of the most influential drivers of long-term market growth. Once viewed as a cyclical corner of the technology sector, chipmakers are now central to artificial intelligence, cloud computing, data centers, electric vehicles, and next-generation connectivity. Investors looking to capture this transformation without betting on a single company have often turned to sector-focused exchange-traded funds, including the Invesco Semiconductors ETF (PSI).
Analysis referenced by Arbitics highlights PSI as a clear example of how concentrated exposure to a powerful long-term trend can significantly outperform the broader market, while also underscoring the importance of understanding sector-specific risk.
A Decade of Strong Performance
Over the past ten years, the Invesco Semiconductors ETF has produced remarkable results. Since late 2015, the fund has delivered a total return of roughly 820%, far exceeding the performance of the broader equity market. Over the same period, the S&P 500 gained approximately 233%, illustrating just how dominant semiconductor stocks have been during this cycle.
Put simply:
- $100 invested in PSI a decade ago would be worth close to $920 today
- $500 would have grown to around $4,600
- Larger long-term allocations would have compounded into substantially higher portfolio value
These figures highlight the power of compounding when paired with a sector that benefits from sustained structural demand rather than short-lived trends.
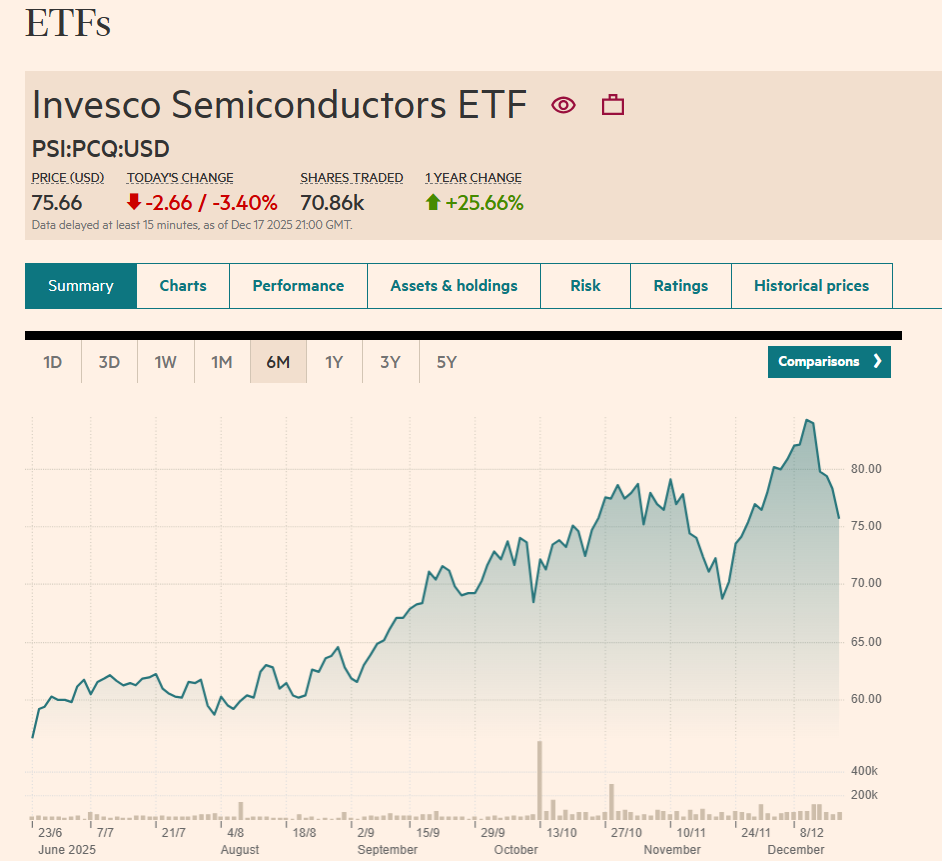
Understanding the Invesco Semiconductors ETF
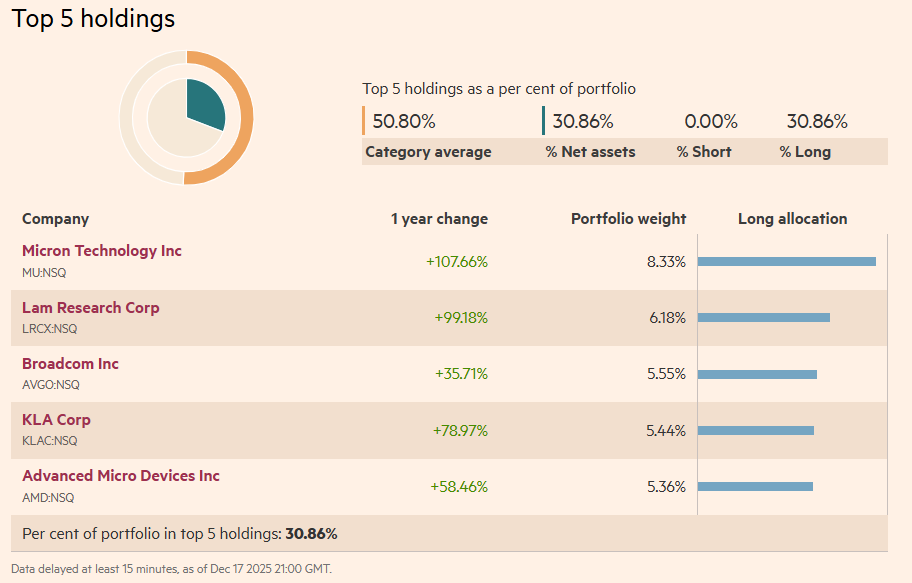
PSI is a sector-specific ETF that holds 30 companies directly linked to the semiconductor industry. The portfolio spans multiple layers of the chip ecosystem, including designers, manufacturers, and equipment providers that enable global chip production.
Through a single investment, PSI provides exposure to:
- Major semiconductor manufacturers
- Chip design leaders
- Companies supplying critical fabrication and manufacturing equipment
- Firms benefiting from AI, cloud infrastructure, and advanced electronics
Rather than attempting to identify the next winning chipmaker, investors gain broad participation in the sector’s overall growth, spreading company-specific risk across multiple holdings.
Why Semiconductors Became a Market Leader
The ETF’s strong performance reflects profound shifts in the global economy. Semiconductors have evolved from optional components into essential infrastructure.
Several long-term forces have driven this change:
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning, which require advanced, high-performance chips
- Cloud computing and data centers, demanding massive and consistent processing power
- Electric vehicles, which rely on semiconductors for power management, safety systems, and automation
- 5G networks and connected devices, expanding chip usage across nearly every industry
As AI adoption accelerates worldwide, semiconductor demand increasingly resembles a multi-year expansion cycle, rather than the boom-and-bust patterns seen in earlier decades.
Diversification Benefits and Their Limits
PSI offers diversification within the semiconductor sector by holding 30 chip-related companies, which helps limit reliance on any single stock. However, sector concentration increases volatility, as semiconductor stocks can face sharp downturns during economic slowdowns or industry cycles.
Many trading experts have advised that investors should balance narrow ETF exposure with broader sector holdings to maintain portfolio stability.
Volatility Comes With the Territory
Higher long-term returns rarely come without periods of discomfort, and PSI’s history reflects that reality. Semiconductor stocks have faced notable drawdowns during market corrections, even when long-term demand remained intact.
However, the past decade demonstrates that investors who stayed invested through volatility were ultimately rewarded. Those who maintained a long-term perspective benefited from the sector’s powerful rebound cycles and compounding growth.
For investors evaluating semiconductor exposure today, the key takeaway is that this is not a short-term trade. It is a strategic, long-term allocation that requires patience during inevitable market swings.
Looking Ahead
The future of the semiconductor industry remains closely tied to global technological progress. AI investment continues to expand, governments are increasing spending on domestic chip manufacturing, and demand for computing power shows little sign of slowing.
That said, future returns may not mirror the extraordinary gains of the past decade. Valuations, competitive pressures, and cyclical risks still matter. PSI’s role is best viewed as a long-term growth component, rather than a guaranteed repeat of past performance.
Final Thoughts
The Invesco Semiconductors ETF serves as a powerful example of how targeted sector investing can dramatically outperform the broader market over time. Turning a modest $100 into nearly $920 illustrates the impact of compounding when aligned with transformative global trends.
Semiconductor-focused ETFs like PSI can play an important role within a diversified portfolio particularly for investors who understand the volatility involved and maintain a long-term investment horizon. While risks remain, semiconductors continue to stand at the center of modern economic growth, making the sector a key force shaping future market returns.
